Published on 2024/07/09 Research powered by Mightex’s Polygon1000 

So Chung Him, Zhang Ting, Wang Qin, Tse, Dennis Y & Feng Pan , Biophysical effects of focused and defocused image stimuli on dopaminergic amacrine cells and AII amacrine cells in the mouse retina. The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, (2024).


Located in the inner nuclear layer of retinas, dopaminergic amacrine cells (DACs) serve as an inhibitory network that modulates signal processing. AII amacrine cells (AII ACs) connect with most subtypes of cone bipolar cells, and changes in AII receptive field properties may dramatically influence signaling in the retinal output.
To explore the possibility that DACs and AII ACs in retinas play a role in detecting focused and defocused signals and driving eyeball growth, it’s important to establish whether these amacrine cells recognize different patterns of stimuli.
The Mightex Polygon1000 system enables the production of annulus/spots at 525 nm wavelength. Polyscan3 software provides stimulation in the form of spot sizes ranging from 30 to 180um in diameter. Annulus is defined as the difference between the outer and inner diameters, from 180-30, 180-60, 180-90, and 180-120, OD – ID in um. The stimuli are presented sequentially according to the diagram.
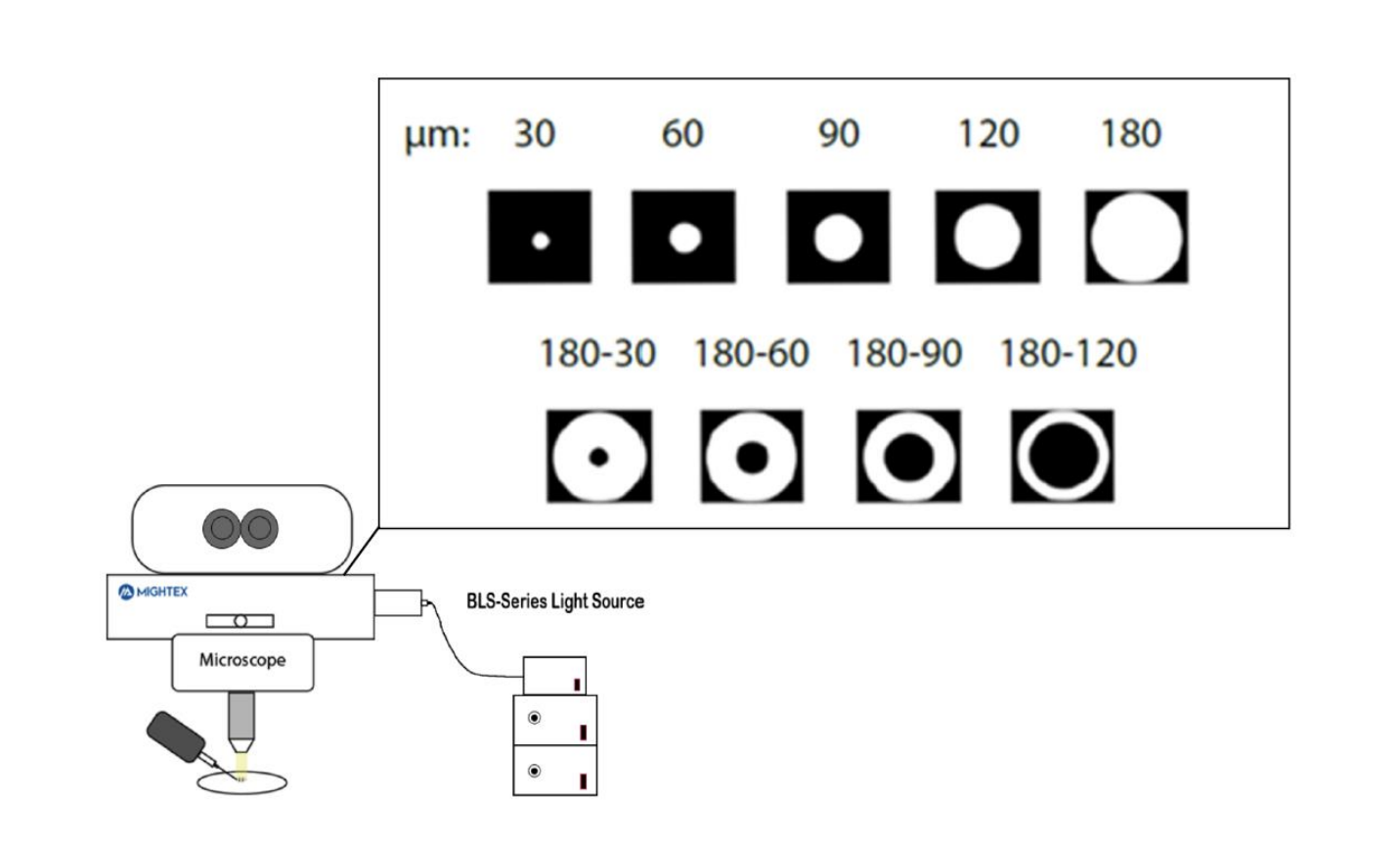
Figure 1. Annulus: Outer diameter – inner diameter
Both DACs and AII ACs can recognize different patterns of stimuli. DACs can detect various patterns of stimuli. To investigate the contribution of both types of amacrine cells to the development of myopia, the next step will involve projecting various images that are focused and defocused, followed by a comprehensive analysis.
References
[1] Banerjee S et al. Increased Connexin36 Phosphorylation in AII Amacrine Cell Coupling of the Mouse Myopic Retina. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Jun 1;14:124.
[2] Schaeffel F. Test systems for measuring ocular parameters and visual function in mice. Front Biosci. 2008;13:4904-4911.
[3] Veruki ML, Hartveit E. Meclofenamic acid blocks electrical synapses of retinal AII amacrine and on-cone bipolar cells. J Neurophysiol. 2009 May;101(5):2339-47.
Author: So Chung Him, PhD
Bio: PhD in School of Optometry , School of Optometry, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong



