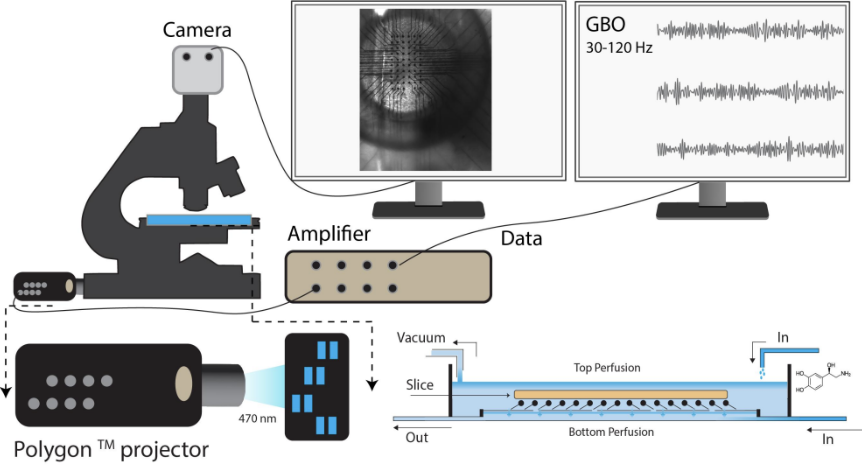
Published on 2024/11/06 Research powered by Mightex’s Polygon1000 

This research was recently presented by Hassan Hosseini at the Lake Conference (2024) in Seattle,USA and was supported by a Mightex Travel Award to promote scientific communication and sharing of research using the Mightex Polygon. Congratulations to Hassan Hosseini! We can’t wait to see more from this exciting project!


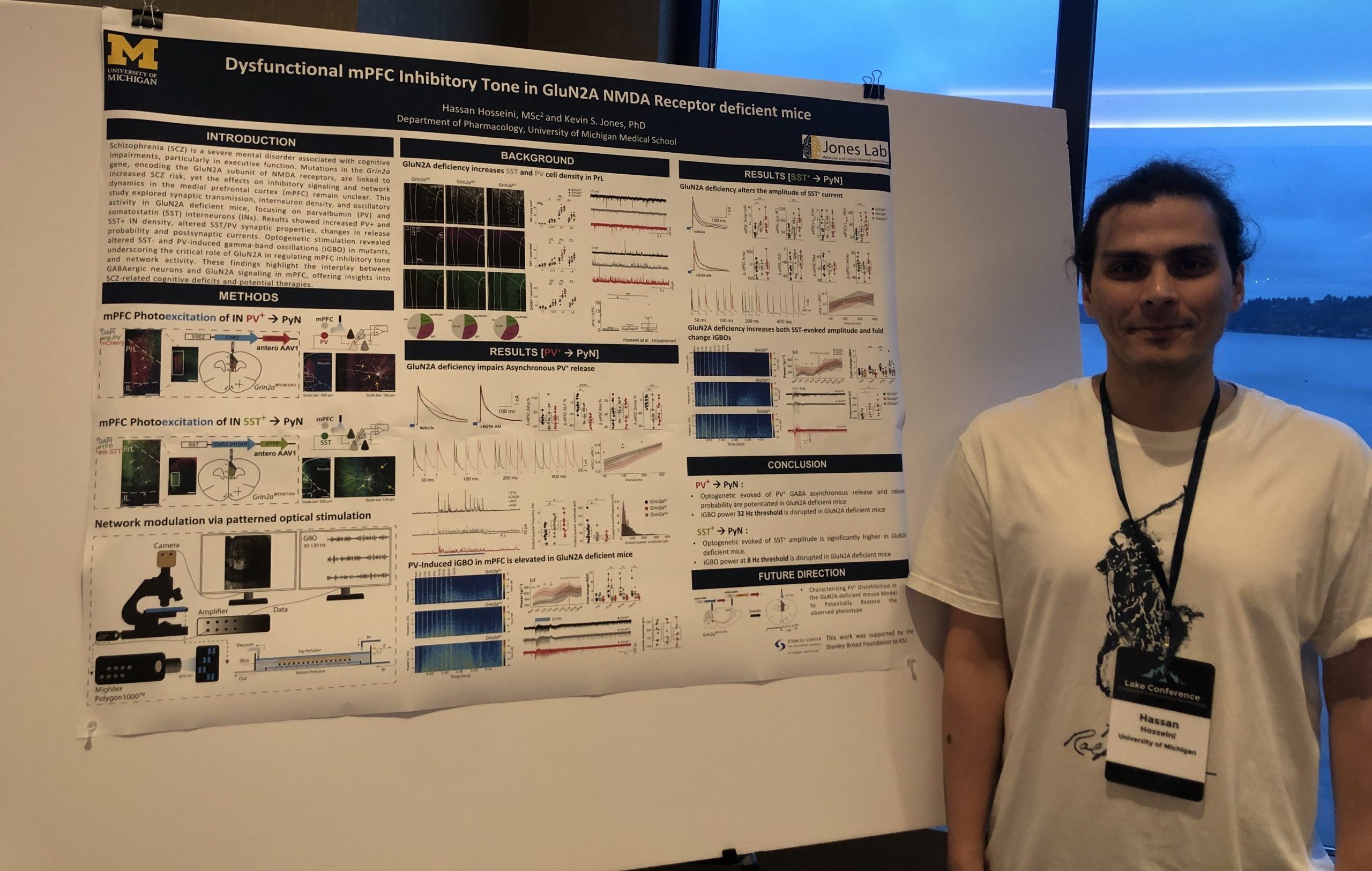
Schizophrenia (SCZ) is a severe mental disorder associated with cognitive impairments, particularly in executive function. Mutations in the Grin2a gene, encoding the GluN2A subunit of NMDA receptors, are linked to increased SCZ risk, yet the effects on inhibitory signaling and network dynamics in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) remain unclear. This study explored synaptic transmission, interneuron density, and oscillatory activity in GluN2A deficient mice, focusing on parvalbumin (PV) and somatostatin (SST) interneurons (INs). Results showed increased PV+ and SST+ IN density, altered SST/PV synaptic properties, changes in release probability and postsynaptic currents. Optogenetic stimulation revealed altered SST- and PV-induced gamma-band oscillations (iGBO) in mutants, underscoring the critical role of GluN2A in regulating mPFC inhibitory tone and network activity. These findings highlight the interplay between GABAergic neurons and GluN2A signaling in mPFC, offering insights into SCZ-related cognitive deficits and potential therapies.
Author: Hassan Hosseini
Bio: Research Laboratory Specialist Associate Intermediate, Department of Pharmacology, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, MI. Advisor: Dr. Kevin Jones.